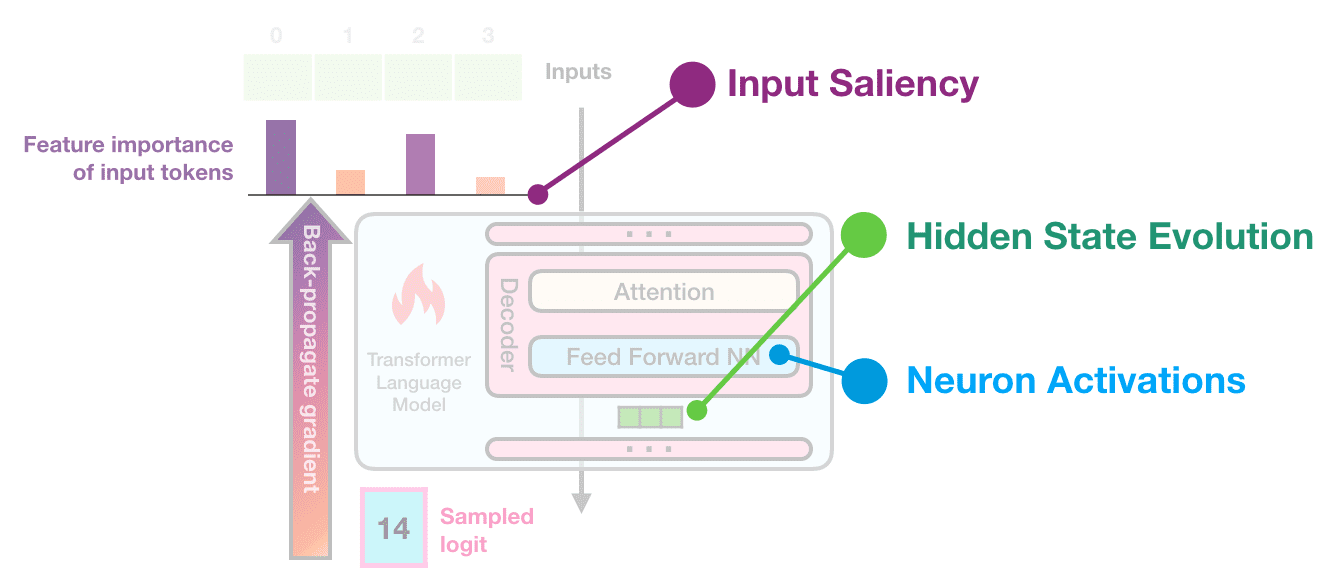
Interfaces for exploring transformer language models by looking at input saliency and neuron activation. Explorable #1: Input saliency of a list of countries generated by a language model Tap or hover over the output tokens: Explorable #2: Neuron activation analysis reveals four groups of neurons, each is associated with generating a certain type of token Tap or hover over the sparklines on the left to isolate a certain factor: The Transformer architecture has been powering a number of the recent advances in NLP. A breakdown of this architecture is provided here . Pre-trained language models based on the architecture, in both its auto-regressive (models that use their own output as input to next time-steps and that process tokens from left-to-right, like GPT2) and denoising (models trained by corrupting/masking the input and that process tokens bidirectionally, like BERT) variants continue to push the envelope in various tasks in NLP and, more recently, in computer vision. Our understanding of why these models work so well, however, still lags behind these developments. This exposition series continues the pursuit to interpret and visualize the inner-workings of transformer-based language models. We illustrate how some key interpretability methods apply to transformer-based language models. This article focuses on auto-regressive models, but these methods are applicable to other architectures and tasks as well. This is the first article in the series. In it, we present explorables and visualizations aiding the intuition of: Input Saliency methods that score input tokens importance to generating a token. Neuron Activations and how individual and groups of model neurons spike in response to inputs and to produce outputs. The next article addresses Hidden State Evolution across the layers of the model and what it may tell us about each layer’s role.